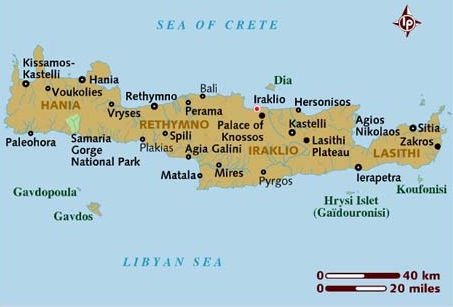
Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete, which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, located on the north shore of the island. As of 2011, the region had a population of 623,065. The Dodecanese are located to the northeast of Crete, while the Cyclades are situated to the north, separated by the Sea of Crete. The Peloponnese is to the region's northwest.
Humans have inhabited the island since at least 130,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic age. Crete was the centre of Europe's first advanced civilization, the Minoans, from 2700 to 1420 BC. The Minoan civilization was overrun by the Mycenaean civilization from mainland Greece. Crete was later ruled by Rome, then successively by the Byzantine Empire, Andalusian Arabs, the Venetian Republic, and the Ottoman Empire. In 1898 Crete, whose people had for some time wanted to join the Greek state, achieved independence from the Ottomans, formally becoming the Cretan State. Crete became part of Greece in December 1913.
The island is mostly mountainous, and its character is defined by a high mountain range crossing from west to east. It includes Crete's highest point, Mount Ida, and the range of the White Mountains (Lefka Ori) with 30 summits above 2000 metres in altitude and the Samaria Gorge, a World Biosphere Reserve. Crete forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece, while retaining its own local cultural traits (such as its own poetry and music). The Nikos Kazantzakis airport at Heraklion and the Daskalogiannis airport at Chania serve international travelers. The palace of Knossos, a Bronze Age settlement and ancient Minoan city, is also located in Heraklion