A = Jugular Vein
B = Right Common Carotid Artery
Carotid ultrasound is a painless and harmless test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the insides of the two large arteries in your neck. These arteries, called carotid arteries, supply your brain with blood. You have one carotid artery on each side of your neck.
Carotid ultrasound shows whether a material called plaque has narrowed your carotid arteries. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. It builds up on the insides of your arteries as you age.
Too much plaque in a carotid
artery can cause a stroke. The plaque can slow down or block the flow of
blood through the artery, allowing a blood clot to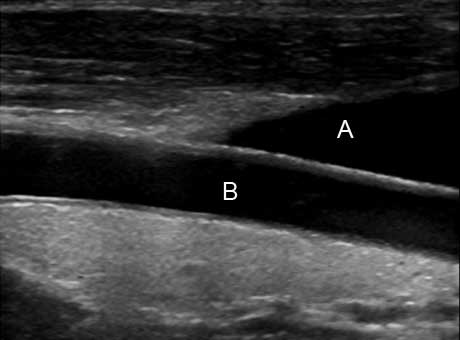 form. A piece of the
blood clot can break off and get stuck in the artery, blocking blood flow
to the brain. This is what causes a stroke.
form. A piece of the
blood clot can break off and get stuck in the artery, blocking blood flow
to the brain. This is what causes a stroke.
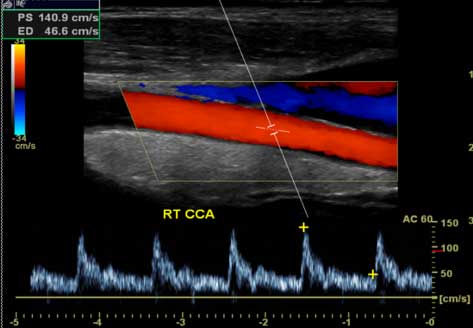
A standard carotid ultrasound
shows the structure of your carotid artery. Your carotid ultrasound test
may include a Doppler ultrasound. Doppler ultrasound is a special
ultrasound that shows the
 movement of blood through your blood vessels.
Your doctor often will need results from both types of ultrasound to fully
assess if there is a problem with blood flow through your
carotid
arteries.
movement of blood through your blood vessels.
Your doctor often will need results from both types of ultrasound to fully
assess if there is a problem with blood flow through your
carotid
arteries.
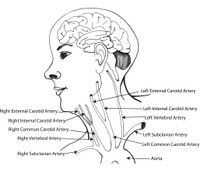
There are 4 major blood vessels that go to the brain: 2 carotid arteries and 2 vertebral arteries. The 2 carotid arteries are in the front part of the neck; these can actually be felt pulsating adjacent to your Adam's apple, just below the angle of the jaw. The 2 vertebral arteries go to the back of the brain and run in the bony portion of the spine.
Note: I was told I would be informed if there were any areas of plaque that needed taken care of. So far so good!
First Payments for Research Projects - Ultrasound for Plaque - Such a Deal!

